Keratoconus is a disease where the cornea of the eye is distorted into a conical shape instead of the usual, even, dome shape. This process of distortion thins the width of the cornea at the center and its lower part, something which causes shortsightedness (myopia) and high and uneven astigmatism (cylinder). In other words, the picture obtained is uneven and even distorted. It is important to note that this disease does not cause blindness, but impacts the quality of life, with respect to driving, reading and quality of vision.
Diagnosis
A diagnosis of Keratoconus is made via imaging and topography of the cornea. The imaging device is digital, samples and checks the surface of the cornea and translates the corneal shape into a map of colors. The warm colors – yellow, orange and red – show the curved areas of the cornea, while the cold colors – green and blue – show the flatter parts of the cornea.
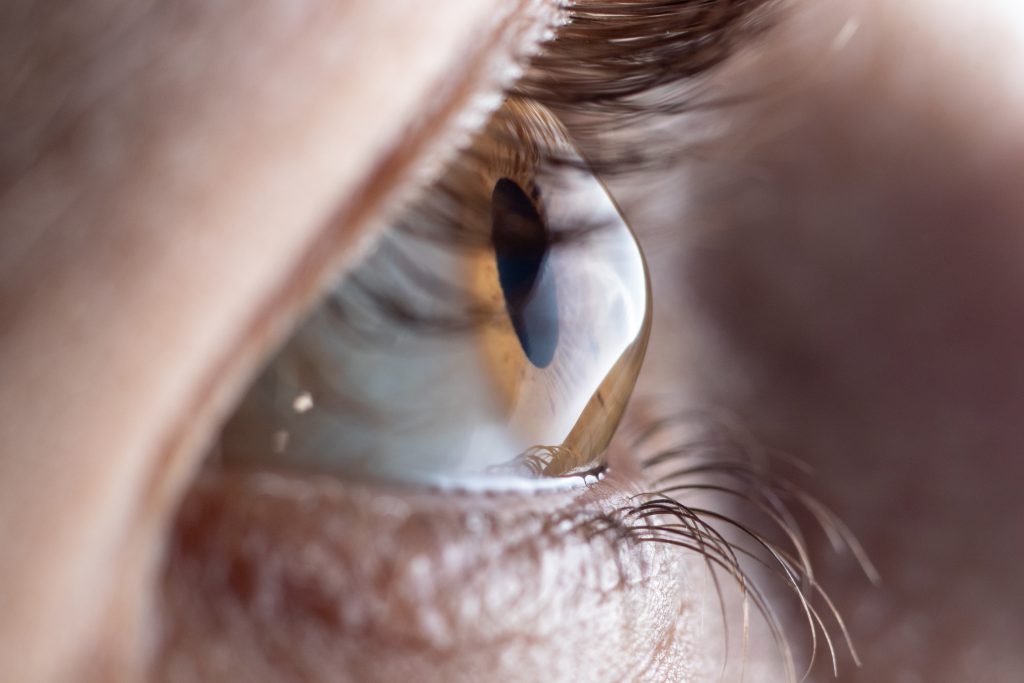

Formation of Keratoconus
The cornea is composed of layers, which are linked together in order to preserve its dome-like shape. Weakening of these links causes sliding of the corneal layers one on top of the other, which causes the narrowing of the cornea. The narrower region of the cornea begins to protrude as a result of the positive pressure which exists in eyeball and the protrusion created causes distortion of vision.
The most common cause of the formation of Keratoconus is the rubbing of the eyes.
There is a genetic (heritable) component, so for people who discover that they have Keratoconus, it is recommended that their first-degree relatives (brothers, sisters, children) are brought for examination.
An additional risk factor is that of recurring eye infections (mainly allergic inflammation), which is likely to be due to the irritation caused by the inflammation which encourages the rubbing of the eyes.
For most people, this disease starts in adolescence and develops slowly, until their thirties. It is important to remember that the rate of development of Keratoconus varies from person to person.
Types of treatment for Keratoconus
There are several possible treatments for the disease, but obviously for different stages of the disease, different treatments will be suitable.
The treatment types are divided into those that improve vision and those that stop the progression of the disease.
Treatment with contact lenses
In the early stages of the disease, treatment with spectacles or contact lenses is possible. There are types of contact lenses which are made to suit the patient. An optometrist who is trained in the subject orders them himself. The potential disadvantages of contact lenses are allergies and recurring infections.
Surgical Treatment – Ring Implantation
Ring implantation is a reversible process. The implanted rings are arch-shaped and placed in the cornea. Their purpose is to decrease the convex curvature of the cornea and straighten the area, something which will enable the use of contact lenses. It is important to state that the process is not always suitable, only in cases where the Keratoconus is with mild to moderate convex curvature. Therefore, they do not cure, rather improve to a certain extent, the convex curvature of the cornea, and thereby improve vision. For this procedure there are also complications such as an inflammatory reaction or an infection around the implanted ring.
Corneal Implantation
Corneal implantation is a surgical procedure. Its success rate stands at around 95% for people suffering from Keratoconus. During surgery, the damaged part of the cornea is removed, and in its place, the cornea of a recently deceased individual is implanted. There are two kinds of implants: a partial corneal implant and a full corneal implant.
The duration of surgery is between an hour and a half to two hours, sometimes performed under local anesthetic and sometimes under general anesthetic.
Complications and risks that may arise from this surgery are an increase in intraocular pressure, rejection of the corneal implant and in rare cases, a recurrence of Keratoconus or a complete loss of vision.
After surgery, wearing spectacles or contact lenses is still required for correction of vision.
Crosslinking Treatment
Collagen Crosslinking is a treatment whose purpose is to stop the progression of Keratoconus. The treatment is performed under a local anesthetic via drops. The objective of this treatment is to harden the cornea and strengthen it by dropping Riboflavin (vitamin B2) onto the surface of the cornea, while simultaneously administering UV-A radiation. The combination of these two actions causes internal crosslinking between collagen molecules in the cornea, thus strengthening the links between the corneal layers.
This treatment has been available in Israel and globally for more than 10 years, and the results of large research studies on the subject show that it can slow or stop the progression of the disease.
The percentage experiencing complications for this procedure is very low, but complications can occur, including corneal infection or inflammation. These symptoms can be treated with antibiotics or anti-inflammatories.